中国生命周期影响评估中环境 PM2.5 健康损害的本土化特征因子
Qiao Ma, Renxiao Yuan, Shan Wang, Yuchen Sun, Qianqian Zhang, Xueliang Yuan, Qingsong Wang, Congwei Luo
摘要
生命周期评估(LCA)是一种广泛使用的量化环境影响的方法,而生命周期影响评估(LCIA)是生命周期评估的重要步骤,也是不确定性的主要来源。表征因子(CF)是 LCIA 模型中的关键要素。在中国,环境 PM2.5 导致的健康损失是 LCIA 结果的一个重要方面,但一般采用全球模型开发的特征因子进行评估,因此仍需结合本地化考虑因素和最新信息,以便在中国进行更精确的应用。在本研究中,我们将大气化学传输模型 GEOS-Chem、包含中国队列研究的暴露-反应模型 GEMM 和最新的本地数据结合起来,开发了中国环境 PM2.5 健康损害 LCIA 的本地化 CFs。结果表明,中国四种主要 PM2.5 前体物的 CFs 均表现出显著的区域间差异和月度差异。与目前使用的CFs相比,我们的结果普遍高出一个数量级,并且显示出不同的空间分布,这表明在中国,环境PM2.5造成的健康损害在LCIA中被低估了,为了在LCIA和LCA研究中获得更准确的结果,需要采用本土化的CFs。
本文章由计算机程序翻译,如有差异,请以英文原文为准。
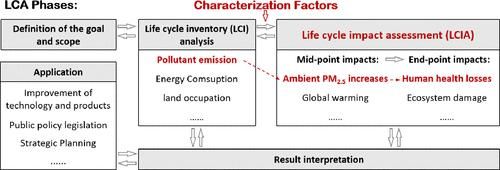
Indigenized Characterization Factors for Health Damage Due to Ambient PM2.5 in Life Cycle Impact Assessment in China
Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a broadly used method for quantifying environmental impacts, and life cycle impact assessment (LCIA) is an important step as well as a major source of uncertainties in LCA. Characterization factors (CFs) are pivotal elements in LCIA models. In China, the health loss due to ambient PM2.5 is an important aspect of LCIA results, which, however, is generally assessed by adopting CFs developed by global models and there remains a need to integrate localized considerations and the latest information for more precise applications in China. In this study, we developed indigenized CFs for LCIA of health damage due to ambient PM2.5 in China by coupling the atmospheric chemical transport model GEOS-Chem, exposure–response model GEMM containing Chinese cohort studies, and the latest local data. Results show that CFs of four major PM2.5 precursors all exhibit significant interregional variation and monthly differences in China. Our results were generally an order of magnitude higher and show disparate spatial distribution compared to CFs currently in use, suggesting that the health damage due to ambient PM2.5 was underestimated in LCIA in China, and indigenized CFs need to be adopted for more accurate results in LCIA and LCA studies.
相关文献
二甲双胍通过HDAC6和FoxO3a转录调控肌肉生长抑制素诱导肌肉萎缩
Min Ju Kang, Ji Wook Moon, Jung Ok Lee, Ji Hae Kim, Eun Jeong Jung, Su Jin Kim, Joo Yeon Oh, Sang Woo Wu, Pu Reum Lee, Sun Hwa Park, Hyeon Soo Kim
具有疾病敏感单倍型的非亲属供体脐带血移植后的1型糖尿病
Kensuke Matsumoto, Taisuke Matsuyama, Ritsu Sumiyoshi, Matsuo Takuji, Tadashi Yamamoto, Ryosuke Shirasaki, Haruko Tashiro
相关知识
环境污染与健康风险的评估.pptx
健康风险评估论文
一种影响生育健康的环境因素,常常被忽略,很多人还在中招!
环境是如何影响我们的健康的?
中国人口健康模式变化 环境污染成威胁健康重要因素
环境友好型病媒防治产品的评估.docx
全国政协委员施小明:环境健康风险评估制度全国推广时机成熟
中国环境健康面临的问题及国外经验借鉴
环境健康风险评估,是()对环境中化学、物理、微生物()所产生的潜在健康影响进行综合定性、定量评价的过程。
环境污染对人类健康的综合影响.docx
网址: 中国生命周期影响评估中环境 PM2.5 健康损害的本土化特征因子 https://www.trfsz.com/newsview239010.html
推荐资讯
- 1发朋友圈对老公彻底失望的心情 12775
- 2BMI体重指数计算公式是什么 11235
- 3补肾吃什么 补肾最佳食物推荐 11199
- 4性生活姿势有哪些 盘点夫妻性 10428
- 5BMI正常值范围一般是多少? 10137
- 6在线基础代谢率(BMR)计算 9652
- 7一边做饭一边躁狂怎么办 9138
- 8从出汗看健康 出汗透露你的健 9063
- 9早上怎么喝水最健康? 8613
- 10五大原因危害女性健康 如何保 7828






